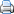White chocolate is a chocolate derivative. It commonly consists of cocoa butter, sugar and milk solids, and is characterized by a pale yellow or ivory appearance. The melting point of cocoa butter, its primary cocoa bean component, is high enough to keep white chocolate solid at room temperature. During the manufacturing process, the dark-colored solids of the cocoa bean are separated from its fatty content (as with milk, semi-sweet, and dark chocolate) but, unlike conventional chocolates, the cocoa solids are not later recombined. As a result, white chocolate contains only trace amounts of the stimulants theobromine and caffeine,[2] while lacking the antioxidant properties or many characterizing ingredients of chocolate, such as thiamine, riboflavin, and phenylethylamine.[3] Often, the cocoa butter is deodorized to remove its strong flavor.
-
"Dark chocolate", also called "black chocolate", is produced by adding fat and sugar to cocoa. It is chocolate with no milk or much less than milk chocolate. The U.S. has no official definition for dark chocolate. Dark chocolate can be eaten as is, or used in cooking, for which thicker, baking bars, usually with high cocoa percentages ranging from 70% to 99% are sold. Dark is synonymous with semisweet, and extra dark with bittersweet, although the ratio of cocoa butter to solids may vary.
- "Semisweet chocolate" is frequently used for cooking purposes. It is a dark chocolate with (by definition in Swiss usage) half as much sugar as cocoa, beyond which it is "sweet chocolate."
- "Bittersweet chocolate" is chocolate liquor (or unsweetened chocolate) to which some sugar (less than a third), more cocoa butter, vanilla, and sometimes lecithin has been added. It has less sugar and more liquor than semisweet chocolate, but the two are interchangeable when baking. Bittersweet and semisweet chocolates are sometimes referred to as 'couverture'. Many brands now print on the package the percentage of cocoa in the chocolate (as chocolate liquor and added cocoa butter). The higher the percentage of cocoa, the less sweet the chocolate is.
- "Couverture" is a term used for chocolates rich in cocoa butter. Popular brands of couverture used by professional pastry chefs and often sold in gourmet and specialty food stores include: Valrhona, Felchlin, Lindt & Sprüngli, Scharffen Berger, Cacao Barry, Callebaut, Chocodate, Chocofig fuel chocolates, and Guittard. These chocolates contain a high percentage of cocoa.
- "Milk chocolate" is solid chocolate made with milk in the form of milk powder, liquid milk, or condensed milk added. In the 1870s, Swiss confectioner Daniel Peter developed solid milk chocolate using condensed milk, but German company Jordan & Timaeus in Dresden, Saxony had already invented milk chocolate in 1839;[2] hitherto it had only been available as a drink.[3] The U.S. Government requires a 10% concentration of chocolate liquor. EU regulations specify a minimum of 25% cocoa solids. However, an agreement was reached in 2000 that allowed what by exception from these regulations is called "milk chocolate" in the UK, Ireland, and Malta, containing only 20% cocoa solids, to be traded as "family milk chocolate" elsewhere in the European Union.[4]"Hershey process" milk chocolate is popular in North America. It was invented by Milton S. Hershey, founder of The Hershey Company, and can be produced more cheaply than other processes since it is less sensitive to the freshness of the milk. The process is a trade secret, but experts speculate that the milk is partially lipolyzed, producing butyric acid, which stabilizes the milk from further fermentation. This compound gives the product a particular sour, "tangy" taste, to which the American public has become accustomed, to the point that other manufacturers now simply add butyric acid to their milk chocolates
| < Prev | Next > |
|---|