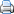Its large, starchy, sweet tasting tuberous roots are an important root vegetable
This plant is a herbaceous perennial vine, bearing alternate heart-shaped or palmately lobed leaves and medium-sized sympetalous flowers. The edible tuberous root is long and tapered, with a smooth skin whose colour ranges between red, purple, brown and white. Its flesh ranges from white through yellow, orange, and purple.
Besides simple starches, sweet potatoes are rich in complex carbohydrates, dietary fiber, beta carotene (a vitamin A equivalent nutrient), vitamin C, and vitamin B6. Pink and yellow varieties are high in carotene, the precursor of vitamin A.
In India, in some regions fasts of religious nature are an occasion for a
change in normal diet, and a total absence from cooking or eating is
held as elective while a normal diet for a fasting day is a light feast
consisting of different foods from usual, amongst which sweet potato is
one of the prime sources of sustainance. Sweet potato is eaten otherwise
too, and a popular variety of preparation in most parts is roasted slow
over kitchen coals at night and eaten with some dressing - primarily
salt, possibly yogurt - while the easier way in south is simply boiling
or pressure cooking before peeling, cubing and seasoning for a vegetable
dish as part of the meal. Usually the preparations for sweet potato are
similar to the blander ones for potato, while the sharper versions -
with more green chilly or red pepper - are reserved for potato.
| < Prev | Next > |
|---|