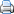It is celebrated on the first day of the Chaitra month to mark the beginning of the New year according to the lunisolar Hindu calendar. It is theorized that Padwa is the origin of the term "Pagwah", a synonymous title used in Guyana and Trinidad for Holi.
On Gudi Padwa, a gudi is found hanging out of a window or otherwise prominently displayed in traditional Maharashtrian households. Gudi is a bright green or yellow cloth adorned with brocade (zari) tied to the tip of a long bamboo over which gathi (sugar crystals), neem leaves[citation needed], a twig of mango leaves and a garland of red flowers is tied. A silver or copper pot is placed in the inverted position over it. This gudi is then hoisted outside the house, in a window, terrace or a high place so that everybody can see it.
Some of the significances attributed to raising a Gudhi are as follows:
Gudhi symbolizes the Brahmadhvaj (translation: Brahma’s flag) mentioned in the Brahma Purana, because Lord Brahma created the universe on this day. It may also represent Indradhvaj (translation: the flag of Indra).[5]
Mythologically, the Gudhi symbolizes Lord Rama’s victory and happiness on returning to Ayodhya after slaying Ravan. Since a symbol of victory is always held high, so is the gudi (flag). It is believed that this festival is celebrated to commemorate the coronation of Rama post his return to Ayodhya after completing 14 years of exile.
Maharashtrians also see the Gudhi as a symbol of victory associated with the conquests of the Maratha forces led by Chhatrapati Shivaji. It also symbolizes the victory of King Shalivahana over Sakas and was hoisted by his people when he returned to Paithan.
The Gudhi is positioned on the right side of the main entrance of the house. The right side symbolizes active state of the soul.
On the festive day, courtyards in village houses will be swept clean and plastered with fresh cow-dung. Even in the city, people take the time out to do some spring cleaning. Women and children work on intricate rangoli designs on their doorsteps, the vibrant colours mirroring the burst of colour associated with spring. Everyone dresses up in new clothes and it is a time for family gatherings.
Traditionally, families are supposed to begin the festivities by eating the bittersweet leaves of the neem tree. Sometimes, a paste of neem leaves is prepared and mixed with dhane, gul/gur (known as jaggery in English), and tamarind. All the members of the family consume this paste, which is believed to purify the blood and strengthen the body’s immune system against diseases.
Maharashtrian families also make shrikhand and Poori on this day. Konkanis make Kanangachi Kheer, a variety of Kheer made of sweet potato, coconut milk, jaggery, rice flour, etc. and Sannas.
| < Prev | Next > |
|---|